Programming Software
Programming software is software that helps the programmer in developing other software. Compilers, assemblers, debuggers, interpreters, etc. are examples of programming software. Integrated development environments (IDEs) are combinations of all these software.
Programming software is also known as a programming tool or software. development tool.
Programming software is a sub-category of system software but according to some sources it is stated as a separate category of software along with application and system software.
Programming Language
A programming language is a formal language comprising a set of instructions that produce various kinds of output. Programming languages are used in computer programming to implement algorithms.
Most programming languages consist of instructions for computers. There are programmable machines that use a set of specific instructions, rather than general programming languages.
Consolidation and growth
The 1980s were years of relative consolidation. C++ combined object-oriented and systems programming. The United States government standardized Ada, a systems programming language derived from Pascal and intended for use by defense contractors. In Japan and elsewhere, vast sums were spent investigating the so-called "fifth-generation" languages that incorporated logic programming constructs.[40] The functional languages community moved to standardize ML and Lisp. Rather than inventing new paradigms, all of these movements elaborated upon the ideas invented in the previous decades.
One important trend in language design for programming large-scale systems during the 1980s was an increased focus on the use of modules or large-scale organizational units of code. Modula-2, Ada, and ML all developed notable module systems in the 1980s, which were often wedded to generic programming constructs.[41]
The rapid growth of the Internet in the mid-1990s created opportunities for new languages. Perl, originally a Unix scripting tool first released in 1987, became common in dynamic websites. Java came to be used for server-side programming, and bytecode virtual machines became popular again in commercial settings with their promise of "Write once, run anywhere" (UCSD Pascal had been popular for a time in the early 1980s). These developments were not fundamentally novel; rather, they were refinements of many existing languages and paradigms (although their syntax was often based on the C family of programming languages).
Fourth-generation programming languages (4GL) are computer programming languages that aim to provide a higher level of abstraction of the internal computer hardware details than 3GLs. Fifth-generation programming languages (5GL) are programming languages based on solving problems using constraints given to the program, rather than using an algorithm written by a programmer.
Syntax
A programming language's surface form is known as its syntax. Most programming languages are purely textual; they use sequences of text including words, numbers, and punctuation, much like written natural languages. On the other hand, there are some programming languages which are more graphical in nature, using visual relationships between symbols to specify a program.
The syntax of a language describes the possible combinations of symbols that form a syntactically correct program. The meaning given to a combination of symbols is handled by semantics (either formal or hard-coded in a reference implementation). Since most languages are textual, this article discusses textual syntax.
Programming Language and Different Types
Types of Programming Languages
The different types of programming languages are discussed below.
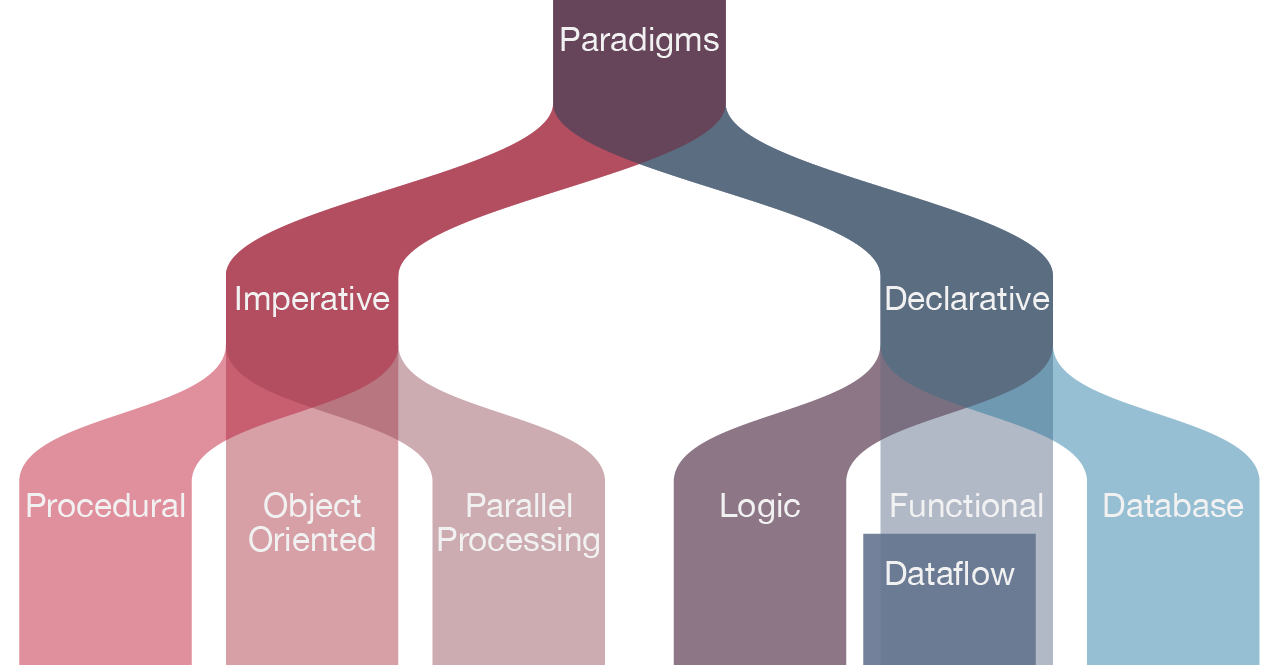
- Procedural Programming Language. ...
- Functional Programming Language. ...
- Object-oriented Programming Language. ...
- Scripting Programming Language. ...
- Logic Programming Language. ...
- C++ Language. ...
- C Language. ...
- Pascal Language.














0 Comments
Please do not send any spam links in the comment box.